 Matthew P. Murphy
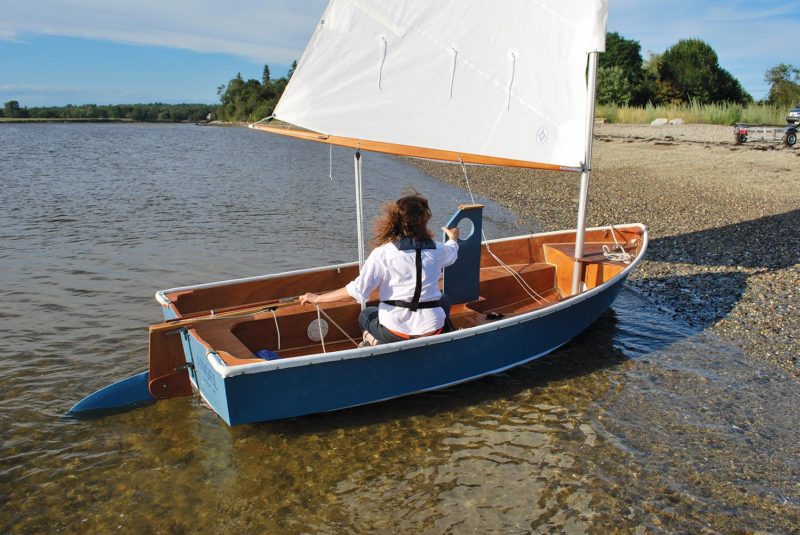
Matthew P. MurphyThe Spindrift series of dinghies from B&B Yacht Designs promises a range of capable yacht tenders that offer plenty of sailing excitement. Here we see a 12’ model built by Meredithe Stuart-Smith of Castine, Maine.
Here we have one member of a family of boats—four in all—doing business under the name of Spindrift and designed by Graham Byrnes of Vandemere, North Carolina. The very first Spindrift was a 10-footer, and was meant purely as a tender to a larger yacht. As Byrnes tells the story on his website, “Not long after the first few were built, we were invited to take part in a race for yacht tenders with a maximum length of 10′. There were dinghies of every description: Trinkas, Connies, Dyers all were represented, as well as some less-well-known brands—and a few custom boats.”
Spindrift trounced the fleet—so much so that there was a mass exodus of dinghies from the local yacht club, and a flurry of Spindrift construction. The word spread to other parts of the country, and more models followed. Today, the lengths are 9′, 10′, 11′, and 12′, and you can choose nesting versions for all but the 12-footer. “Nesting” refers to the boat’s ability to be separated into two pieces—a bow and stern section—with the bow portion turned around and nestled into the stern sections. The result is a tidy package that can be carried on the deck of a small yacht. The rig options include a cat for the 9′, 10′, and 11′ models, and sloop or cat for the 11′ and 12′ ones. To date, Byrnes has sold 1,025 sets of plans.
“A Spindrift,” writes Byrnes, “is a very good investment if you have a junior sailor in your family. Unlike many dinghies used as trainers (such as the Optimist), you do not ‘outgrow’ a Spindrift. While the boat is very suitable for children and inexperienced adults, in the hands of a good competitive sailor it offers the challenge of top-end racing.” Byrnes also intended for the boat to carry a small outboard, which he says it does very well.
The forgiving nature of the boat and its top-end potential are what drew Meredithe Stuart-Smith to Spindrift. A resident of Castine, Maine, Stuart-Smith had taken a sailing course at WoodenBoat School several years ago, and now she wanted a boat in which to hone her new sailing skills. What boat, she wondered, would be adequate for the local conditions, and under 12′ so she could store it on land at the local yacht club? She called Graham Byrnes’s shop and spoke with his wife, Carla, who mentioned the Spindrift—which, as it happened, was to be the subject of an upcoming class at WoodenBoat School.
Stuart-Smith was intrigued, but a little concerned about her limited capacity with woodworking tools, and she shared this concern with Carla.
“Honey,” Stuart-Smith recalls Carla responding, “there are women who could not get out of their Maiden form bras who could build one of these.”
“So,” says Stuart-Smith. “I came, I built, and I sailed.”
 Matthew P. Murphy
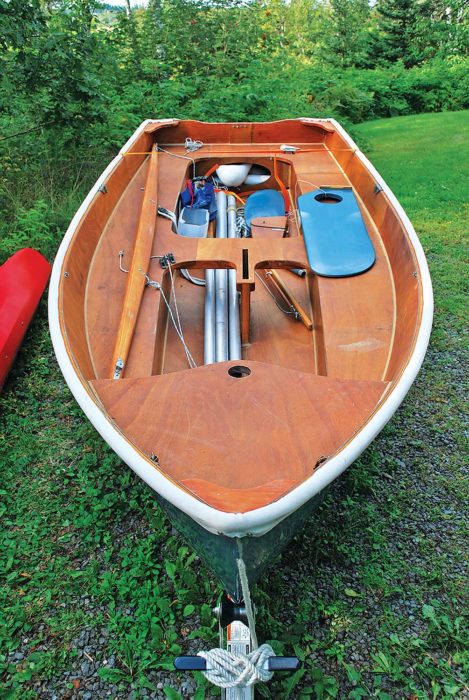
Matthew P. MurphyThe 12′ Spindrift’s spars and blades all stow tidily in the boat for easy trailering.
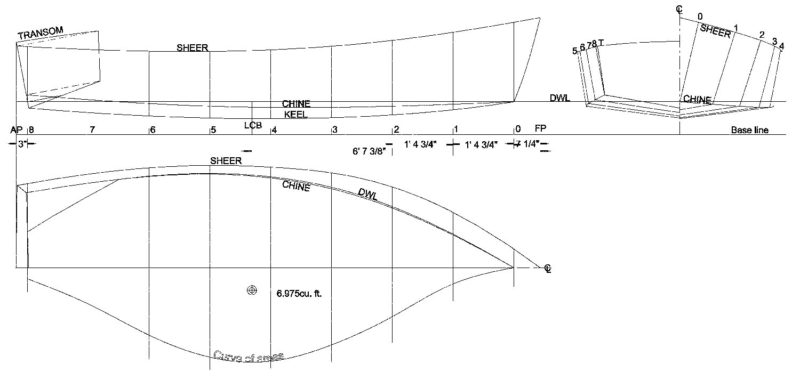
The construction is stitch-and-glue—a process that has as much in common with sewing as it does with traditional boatbuilding. In sewing, the curved edges of flat sheets of fabric are stitched together to yield a sometimes-complex three-dimensional shape. In stitch-and-glue boatbuilding, flat sheets of plywood are cut to precisely curving shapes, and the edges of them “sewn” together to yield a hull. The sewing is commonly done with copper wire or cable ties, and the seams are then “taped” together with fiberglass set in epoxy. There are nuances in this gluing-together job, such as the filleting of seams to eliminate hard inside corners and allow the ’glass to properly bridge the joint, but the process is rather simple and the rewards quick. Hulls are often stitched together in a day—though require much more work to make them solid and strong.
Stuart-Smith finished her hull in the WoodenBoat School class. After that, the demands of business and family life took over, and she sent the boat to Salt Pond Rowing, a shop operated by WoodenBoat School shop assistant Joe Thompson, who finished it—complete with a distinctive and flawless gunsmoke-blue paint scheme. “I’m sad I didn’t finish the boat,” says Stuart-Smith. “But I knew I couldn’t get it done.”
 Matthew P. Murphy
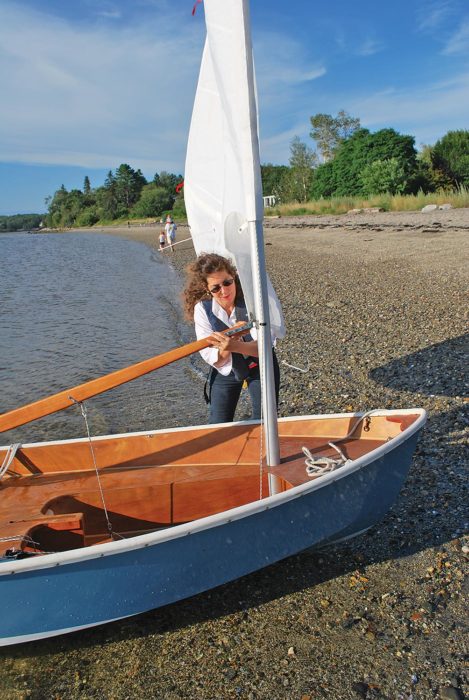
Matthew P. MurphyThe 12′ Spindrift’s two-piece, unstayed aluminum mast is quick and easy to step, and the wooden boom attaches at the gooseneck with a simple slip-on fitting. Rigging takes a matter of minutes.
Stuart-Smith named the boat ANGEL, and four years after its launching, I joined her for a couple of sails from the backshore beach in Castine. This gravelly strand faces west into upper Penobscot Bay, and we arrived at high tide one August evening in a fresh westerly.
Setup was easy. The aluminum mast separates into two sections, which stow neatly and entirely in the boat. The top mast section has a wooden plug inserted in its top. These two sections are easily joined together, and the lightweight spar dropped through the partners and into the step. There is no standing rigging.
The rig is a Bermudan cat, and the sail’s luff is sleeved, like a Laser’s. But unlike that ubiquitous Bruce Kirby–designed board boat—at least the ones I knew growing up—this luff sleeve has a zipper running its length, allowing the sail to be hoisted up the stepped mast, rather than threaded onto the mast on the ground, and the whole thing raised together. That made a big difference in ease of rigging in the breeze that was blowing that evening, for raising that sail Iwo Jima style would have required some manhandling. The zippered luff also allows for quick reefing and shaking-out from the helm position—which is not possible with a standard sleeve luff.
The clew is left to fly while the boat is launched and the boom attached to the gooseneck. Then the rudder is secured, the boat is pointed into the wind, and the outhaul made off. The engine, so to speak, is now idling.
I thought that getting off the beach in the onshore breeze would be a bit awkward—a reflection on me, and not the boat. In the past, I have found daggerboards can be ungainly in this situation. When beam-reaching into a beach, it’s good to have a little bit of blade exposed underwater for as long as possible. And I like to have the board propped in the trunk, ready to press into deep water, when departing in an offshore breeze. But in some of the boats of my youth, the height of that loaded board could impede the progress of the boom across the boat’s centerline, creating an interesting situation—one not unlike the time my ’75 Ford Grenada’s accelerator pedal got stuck under the floor mat as I was cruising down the Nahant causeway in Massachusetts in my high-school years…but I digress. My point is that Byrnes’s careful fitting of the board to clear the boom gave me confidence in the setup. This is a carefully engineered rig— mindful of both the beginner and advanced sailor.
 Meredithe Stuart-Smith
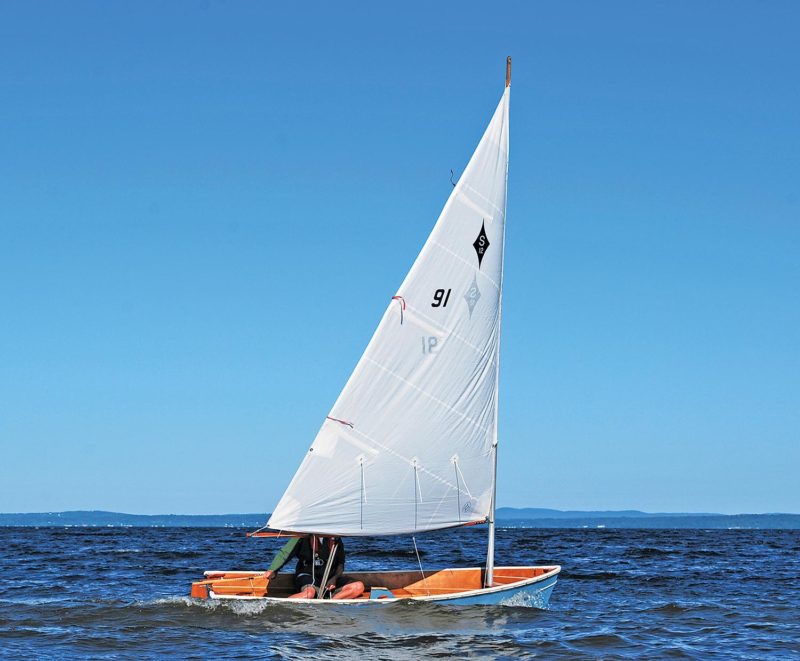
Meredithe Stuart-SmithSpindrift has a rare combination of traits: Exciting sailing, good rowing, and ample volume to serve as a yacht tender. The designer claims that
she handles an outboard motor well, too, though this wasn’t tested for this review.
I got away from the beach, deployed the centerboard, sheeted in, and whoosh: Stuart-Smith had told me that the local kids likened the feeling of her boat to a Laser’s—which I hadn’t sailed for decades. This brought it all back. The boat accelerated quickly, and I settled into the tack and tidied up the mainsheet. Then I tried a few turns. The boat was quick to tack, and sure-footed in jibes.
Stuart-Smith had told me earlier that every one of her sailing outings is like Groundhog Day, referring to the Bill Murray movie in which the protagonist awakes every day to the same circumstances, his life never advancing. She typically sails the boat with a more experienced hand along, and on one solo outing did have the distinct and enlightening pleasure of capsizing. She reports that it was easy to right, and came up only partially filled with water. Much of the interior volume is taken up by the flotation tank seats, so there was minimal bailing. Stuart-Smith has pushed through insecurities about a solo outing, saying that she’s “always doing things that terrify me.” She was bound and determined to take a few passes along the beach that night. And she did. As is often the case in learning, she’d internalized more of the previous year’s lessons than she’d thought. She’d developed instinct. This was proven out in one particular incident when, after the boat was caught in the wind while departing the beach, the sails filled as ANGEL sat still. That’s often the sitting-duck position for a capsize, as all of the sudden wind energy is pressing the boat over, and little or none of it is bleeding off in forward motion. Stuart-Smith leapt to the high side, settled the boat down, and darted off. The rest of the evening was textbook sailing, and putting the boat up took only ten minutes. We lowered the sail, hauled the boat up the beach on its aluminum trailer, popped out the mast, and secured the blades and spars in the bilge. With the hull strapped down, Stuart-Smith and ANGEL headed for the barn.
She told me later that building her own boat was a bit like having a baby. “Afterward, I thought, ‘I’m never doing that again.’” But the confidence she gained from the project soon eclipsed those feelings. “Six months later,” she says, “I was looking at design catalogs. I will definitely build another boat.” ![]()
B&B Yacht Designs, 196 Elm St., Vandemere NC; www.bandbyachtdesigns.com.
 GRAHAM BYRNES, B&B YACHT DESIGNS
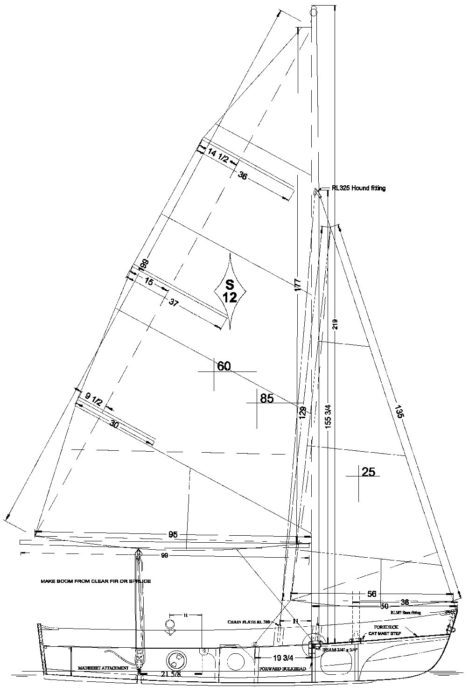
GRAHAM BYRNES, B&B YACHT DESIGNSThe Spindrift dinghy from B&B Yacht Designs is available in four lengths: 9’, 10’, 11’, and 12’. Here we see the 12-footer, the boat tested for this article, with the optional sloop rig.
 GRAHAM BYRNES, B&B YACHT DESIGNS
GRAHAM BYRNES, B&B YACHT DESIGNSParticulars:
LOA 12’0″
Beam 4’6″
Sail area (sloop rig) 85 sq ft
(cat rig) 70 sq ft
Weight 95-120 lbs
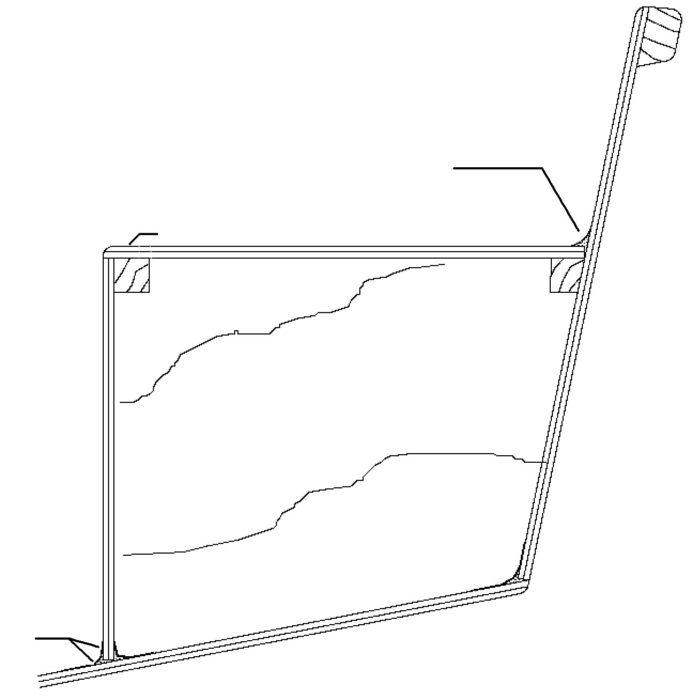




























Let’s shorten the mast by 2′,extend the boom by the same amount. With the original sail plan you still must duck under the boom.Why not make the boom longer? The sail plan lower?
A tall, thin sail, a high-aspect ratio, is more efficient. I had a plastic window sewn in.