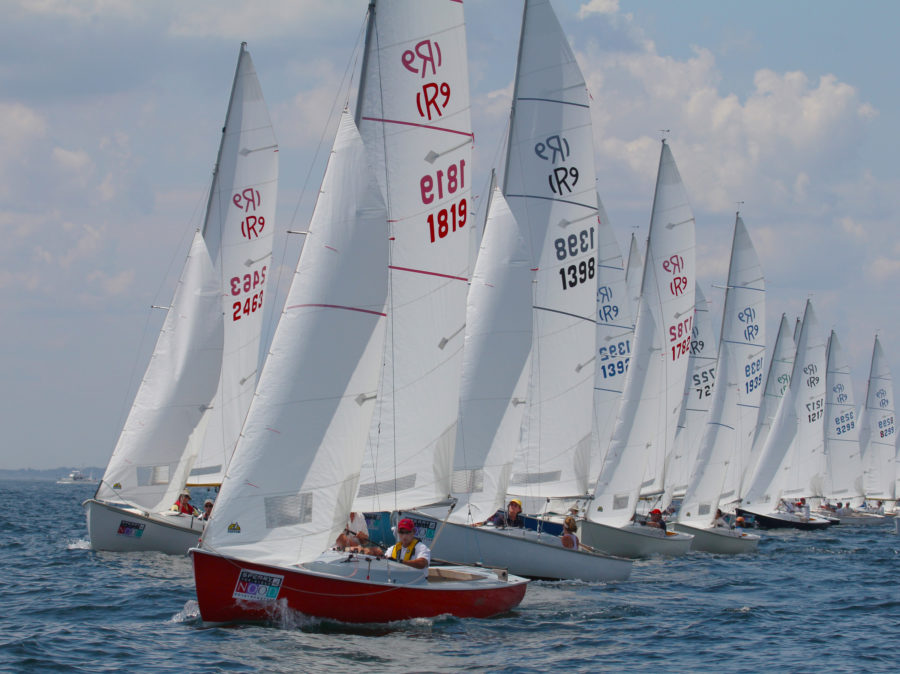
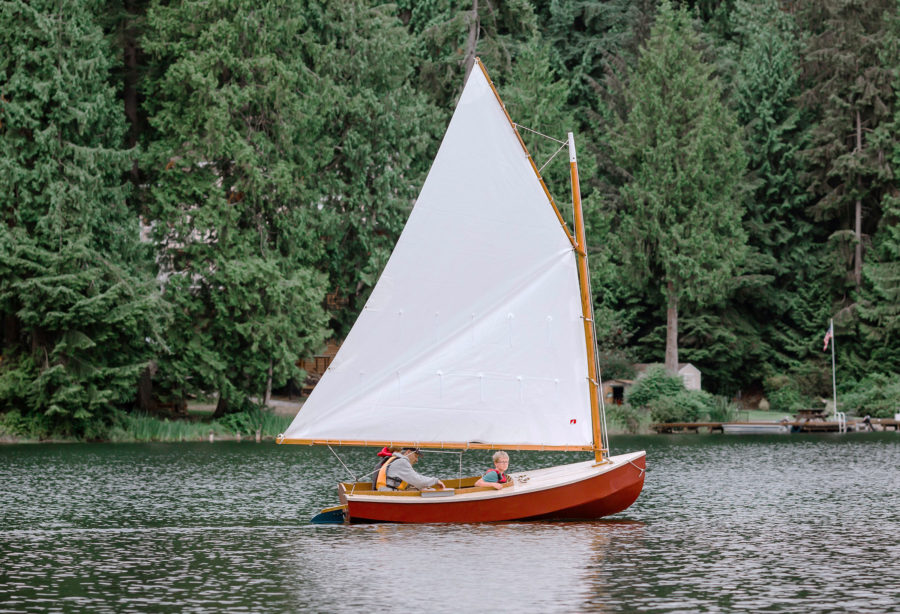
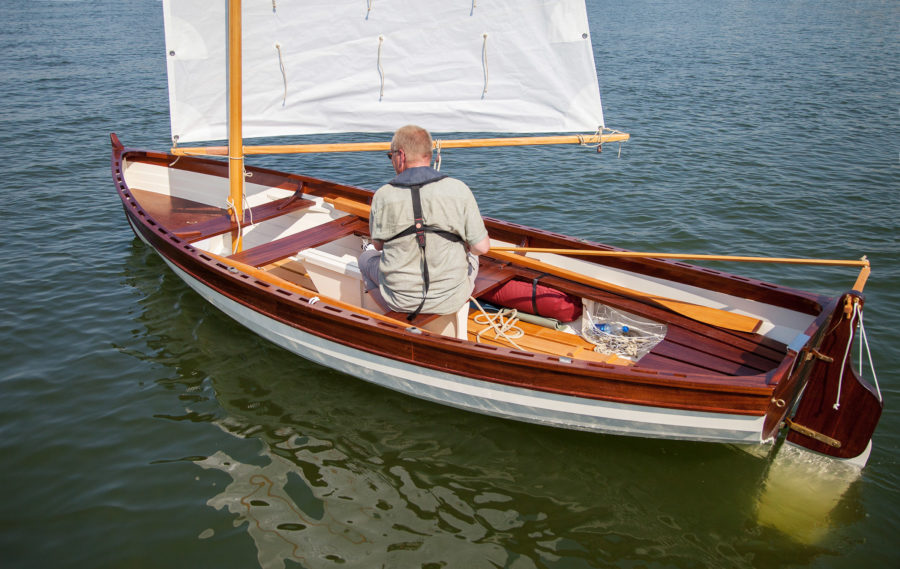
The Oz Goose was love at first sight. Or was it finding a love lost? There is something wonderful about sailing a light, responsive boat. I grew up in The Netherlands in the 1970s and spent all my spare time sailing my 8′ dinghy. Since then, I’ve sailed and often raced dinghies and yachts in many countries, on seas and ocean. But the thing that got me into sailing was the response of a light boat, the chuckle of the water at the bow, and the pride of sailing a boat that was actually mine. Fifty years later, I am as hooked on my Oz Goose as I was on that first dinghy.The Oz Goose is a squarish plywood sailing dinghy measuring 12′ long and 4′ 2″ wide. The “Oz” in its name indicates the nationality of the designer, Michael Storer, who hails from Australia. The Oz Goose is one of the many boats inspired by the Bolger Brick. The pilot version of the Goose was 8′ long and 4.2′ wide; later versions were the current size, 12′ by 4′ 2″. Only a handful of prototypes were built, but in 2014, when Texan sailor Ian Henehan started posting videos of an early Goose planing up to 12 knots in moderate wind, the design drew sailors’ attention around the world. It even surprised Michael that his “experiment” could sail so fast and so well. A MK2 version was developed, with a simplified construction method that made the boat lighter. With new plans available, the Oz Goose soon appeared in Europe, North America, Asia, and Australia. The Oz Goose fleet and community grew quickly through Family Boatbuilding Weekends, when families and community groups can build boats for themselves in just a few days. Sailing clubs popped up; I joined one that regularly brings together more than 20 Oz Goose boats to sail for fun and competitive events.The plans come in the form of a 115-page manual illustrated with color photographs and a wealth of drawings. Measured drawings provide the shapes of the plywood pieces and the easy-to-follow instructions cover almost everything in detail. In addition to the instructions provided for the standard timber-framed construction, there are clearly marked directions for those who prefer to use fillets of thickened epoxy at the intersections of the panels; filleted joints can save time and may be cheaper. The build doesn’t require many tools: pencils and measuring tapes, a cordless drill/screwdriver to put in temporary screws, a jigsaw, and a hand plane. A random-orbit sander speeds finishing work. When we encountered problems, the Goose Facebook group proved very useful with detailed answers in a few hours or overnight, and there are now also some excellent YouTube videos with coverage of specific sections of the building process. Just search for “Oz Goose sailboat construction.”
Join The Conversation
We welcome your comments about this article. If you’d like to include a photo or a video with your comment, please email the file or link.
Comments (7)
Leave a Reply
Stay On Course
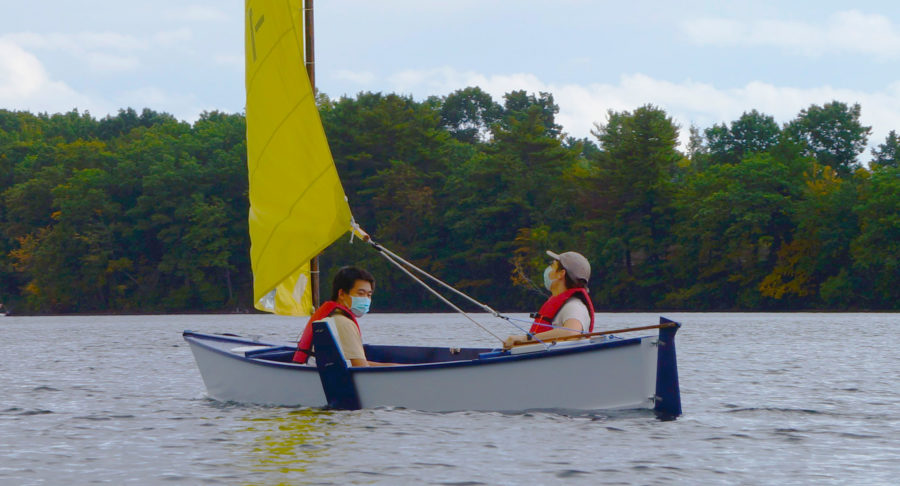
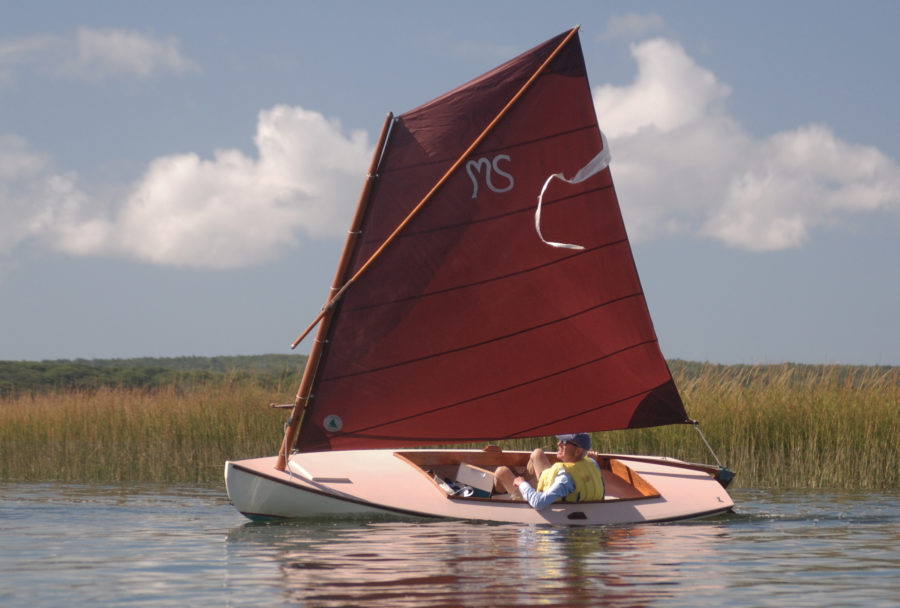



























Thank you for putting this article together, Chris and team.
Also a big thanks to Thom Kleiss. I had the pleasure to sail in company with him several times—he even beat me in some of our regular races. He has just departed the Philippines with his beautiful varnished Oz Goose (the one with blue sail in the article) in a huge plywood box being shipped to Ireland.
We were joking that the box would make an amazing MEGA Goose with a bit of added rocker!
Michael Storer
I love your article. I sail an East port Pram. It has a bit of a rocker. I would intersted in seeing the MEGA as I need room to add a cubby and sleep on board.
Cheers
That version has been designed. See Duckworks for the Goose Explorer.
Very interesting observations about the supposed “bad tack” of the balanced lug rig. I noticed the same thing on my old Caledonia Yawl: the bad tack was better up wind than the good tack.
Following up on the “bad tack” surprising phenomenon, I wonder what would be the affect of putting the daggerboard slot to one side or the other. It would open up a lot of space.
See Michael Storer’s website.
Bolger insisted that boats don’t notice an off-center board, nor an off-center rig. Your idea should work fine.