Seventy years ago, LIFE put the Alcort company on the map when the magazine featured the Sailfish sailboat in an article titled “World’s Wettest, Sportiest Boat,” published in the August 15, 1949 issue. Two years earlier, Alcort had expanded their market from iceboats to the little Sailfish, a lateen-rigged wooden hull that measured just under 12′. The boat was easy to handle, affordable, and offered a sporty, splashy ride to America’s post-war market of recreational sailors.
In 1946, Alex Bryan and Cortlandt Heyniger had combined bits of their first names to create Alcort, Inc., and the first sailboat that they designed, in 1947, was the 11′ 7″ Sailfish, built in Waterbury, Connecticut. The Sailfish had a beam of 31-1/2″, a crew capacity of 300 lbs, and weighed 82 lbs. The volume of air enclosed by the hull and deck made the boat virtually unsinkable. A 65-square-foot lateen sail provided ample power.
 Photographs by the authors
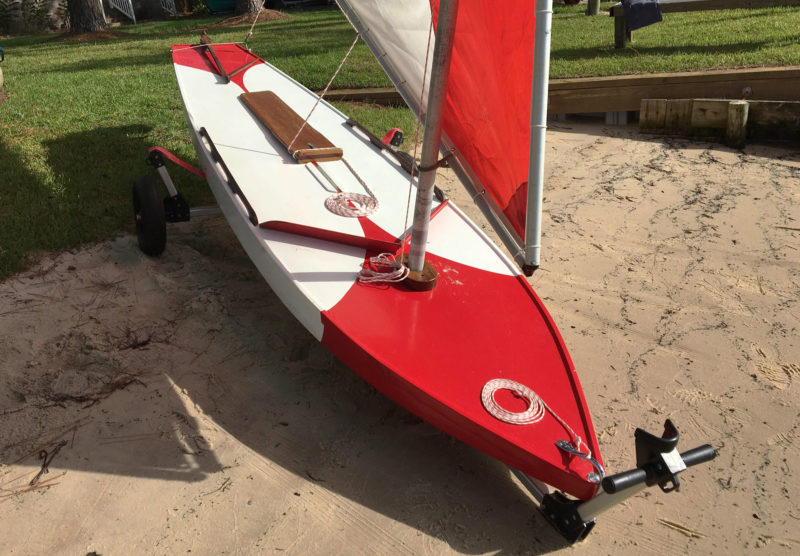
Photographs by the authorsThe authors’ Super Sailfish, ZSA ZSA, is their restoration of a wooden boat built in the 1950s. Here, the varnished daggerboard rests just aft of its slot.
The boat gained immediate popularity after the LIFE article, and within a few years the original design was lengthened to 13′ 7″ and widened a bit to 35-1/2″. The larger Sailfish flew a 75-square-foot sail, weighed 102 lbs, and had a crew capacity of 400 lbs. The original Sailfish was then labeled the Standard Sailfish and the big sister named the Super Sailfish. Production of the two models of Sailfish was brisk, and in 1960 Alcort added a fiberglass version, the Super Sailfish MK II. The MK II hull was the same size as the Super Sailfish, had the same capacity of 400 lbs, and used the same rig, but weighed 98 lbs. Alcort was also producing the wooden Sunfish, which used the same sail rig, daggerboard, and rudder as the Super Sailfish line, and a fiberglass Sunfish with a longer daggerboard and taller transom.
The Alcort literature promised the Sailfish would deliver “thrilling speed, brilliant performance, perfect portability, and swamp-proof safety.” The hull, deck, and frames were made of marine plywood, with mahogany sides, transom, rudder, tiller, and daggerboard. Wilcox and Crittenden in nearby Middletown manufactured the bronze and brass fittings for all of the Alcort boats. The spars on the original Sailfish were cut from Sitka spruce, mid-generation masts were a hybrid aluminum base with wooden top, and spars from the late 1950s on were aluminum.
Alcort offered the Standard Sailfish, Super Sailfish, and Super Sailfish MK II as factory-built boats, and they sold precision-cut knockdown kits for a wooden Sailfish through the late ’50s through the mid-’60s. The Standard Sailfish was phased out in the mid-’60s and the Super Sailfish kit was last seen in the late ’60s. Along the way, a two-page set of plans was produced by Alcort with measurements and a materials list for the frames, hull, rudder, daggerboard, spars, and sail. Armed with the plans, an intrepid home builder could build the boat with locally sourced lumber and hardware. We had occasion recently to replace the bottom panels on a factory-built Super Sailfish, and while we had the panels off we validated the measurements in the plans, and all were within a 1/32″ with only one exception. The factory boat’s bow was swept up just under 1″, a design improvement that helped reduce submarining.
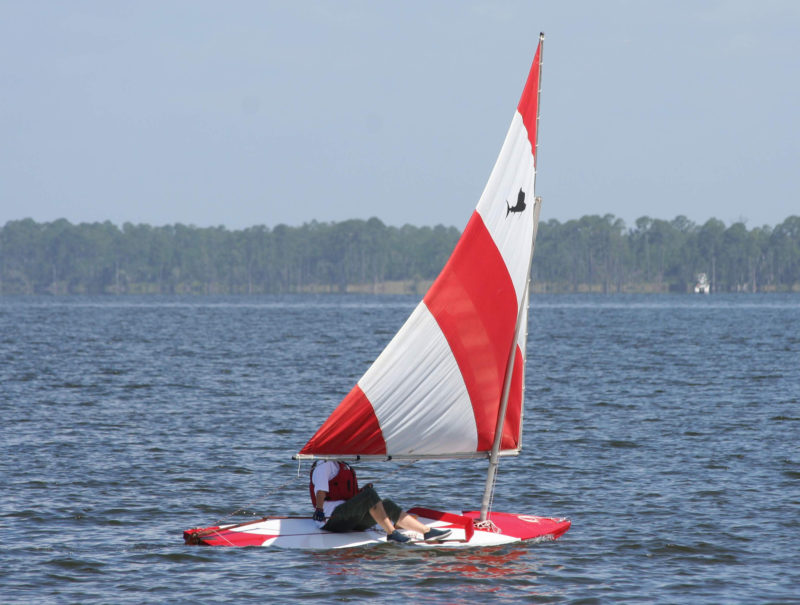

The handrails amidships have an important role as foot bracing to keep the sailor from sliding off the deck when the boat heels.
The Sailfish kits came with all of the wood, hardware, sails, and line needed. Finishing kits with primer, putty, paint, and varnish could be purchased as well. Alcort provided eight pages of well-written instructions with 16 photos. The first two pages of the instructions contained a list of parts included in the kit with numbered photos. The hull was assembled upside down using the shipping crate as a strongback. The first step was to attach the 13′ 3-3/4″ deck longeron to the stem, the seven frames, maststep, daggerboard trunk, and transom. The parts were coated with a sealer, and then screwed together, and the deck was then temporarily attached to the skeleton frame and the solid-wood sides were screwed on, attached first to the stem and pulled into place on the transom with a rope windlass. The inner keel longeron was attached to the frames, and it and the sides were beveled to accept the plywood bottom panels. They were attached with glue and bronze ring-shank nails.
The assembly process was easy. Alcort advertised that it could be done over a weekend with a hammer, rasp, plane, screwdriver, handsaw, square, brace, drill, and bits. A jigsaw would be helpful for building a hull from plans.
The Sailfish delivers on Alcort’s promise of fun. We have sailed all of the models and have only capsized once when a sail caught a puff and the sheet pulled Skipper off the deck. The sheet had no fairlead or cleat, so it was either let go of the sheet or go for a short swim. One sailor joked that “the Sailfish was the boat that you learned to swim on.” The shallow-V hulls of the Super Sailfish and especially the Standard Sailfish with its 31-1/2″ beam, require more balance than the Sunfish. When sailing Sailfish, we tend to sit more amidships and hike out by laying backward at an angle, rather than perpendicular to the centerline. Handrails on the deck serve as foot braces to help maintain control of the boat while hands are busy with the sheet and tiller. Some of the models had a small toerail, which is also helpful for maintaining a grip on the flat, cockpitless deck. The sheet also works as a tether to help keep skippers aboard. Some of the Sailfish had nonskid on the deck, but it quickly wore out pants bottoms. One trick that we’ve come up for tacking is to lean backward instead of forward—while you’re wearing a PFD it is harder to bend forward on a Sailfish than on a Sunfish, which has a cockpit to tuck your legs and feet into.
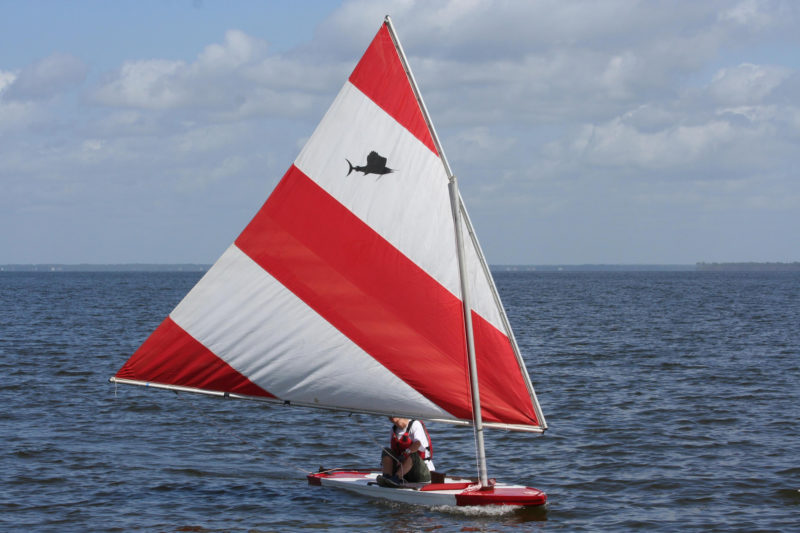

The most recent versions of the spars and mast for the Sailfish were all aluminum.
The Sailfish 65-square-foot sail for the Standard and 75 for the Super are appropriately sized, neither too small to provide fun, even exciting sailing, nor so large as to be overpowering and leading to frequent capsizes. All of the models power up quickly. We’ve found that tacking is improved with a longer daggerboard, similar to the one found on the 1960s fiberglass Sunfish. The mast is easy to step and even kids as young as eight can raise the sail. Our Sailfish moves well even in the lightest of breeze; we enjoy the fingertip control on the tiller and setting coffee cups set on deck, without them sliding over the side. Once the breeze picks up to 5–8 knots, a little more activity is needed to balance the boat and get through tacks smoothly. At 10–12 knots we are moving quickly to stay on course and work the puffs, and above 12 knots we have sailed the Super Sailfish with two on board, one at the tiller and the other serving as movable ballast.
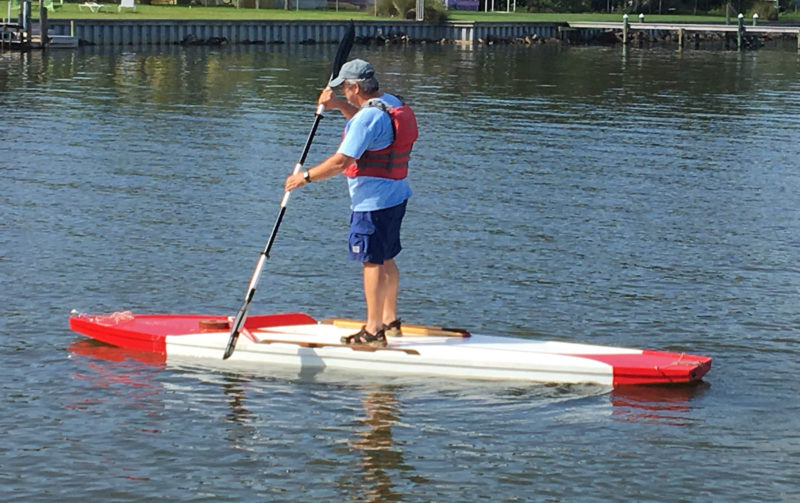

With the sailing rig left ashore, or even stowed on deck, the Super Sunfish serves nicely as a stand-up paddle board.
Alcort made a lot of promises with the Sailfish and delivered on all of them. We’ve even come up with a few more uses for the boats. The Sailfish, with its deck unbroken by a cockpit, makes a respectable stand-up paddleboard, and with a 400-lb capacity, it is well suited for larger paddlers or for an adult taking little crew members out paddling. The deeper hull design has a greater capacity than a normal paddleboard and makes for a very stable platform. The small keel strip helps the boat track straight under paddle power. We can paddle our MK II out in flat calm, and set sail if the wind picks up. I took the hull out once with a low-slung beach chair lashed to the handrails, and it made a fine sit-on-top kayak, a very useful fishing platform or picnic boat. We have also seen folks add outriggers and take their pets out for a ride with plenty of room for the whole pack.
The Sailfish is a proven design. Alcort made thousands of them, and there are still many good boats out there. As the big sisters to the still-available Sunfish, they share most of the same parts, including the sail rig and daggerboard, so building a hull would be an easy way to get into small-boat sailing. The ease of portability and small storage footprint make the Sailfish a fun boat. It’s a nice swim platform for kids, and a wet, wild ride for adults. The up-front investment is minimal and there are no slip fees necessary—just add water!![]()
Kent and Audrey Lewis blog about and maintain a fleet of vintage Alcorts that include a Standard Sailfish, Super Sailfish, Catfish and a wooden Sunfish, along with several fiberglass Sunfish. They also maintain the Yahoo group Sunfish Sailor and publish The Sunfish Owners Manual.
Sailfish Particulars
[table]
Length/11′ 7″
Beam/31.5″
Weight/82 lbs
Capacity/300 lbs
Sail Area/65 sq. ft.
[/table]
Super Sailfish Particulars
[table]
Length/ 13′ 7″
Beam/35.5″
Weight/102 lbs
Capacity/400 lbs
Sail Area/75 sq. ft.
[/table]
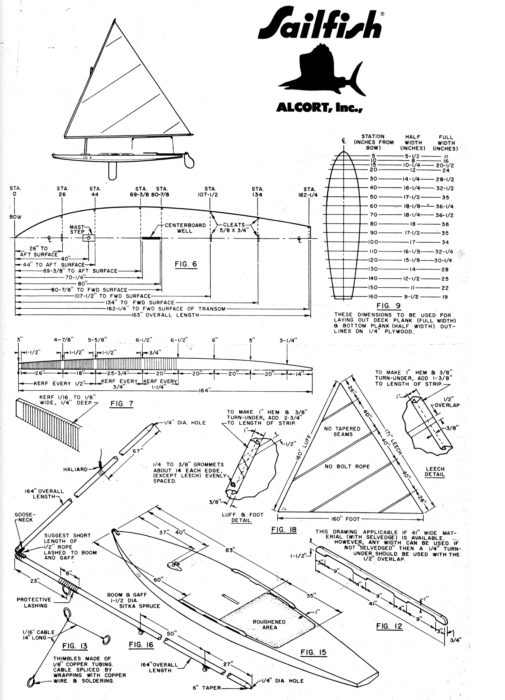 Laser Performance
Laser PerformanceSuper Sailfish with offsets
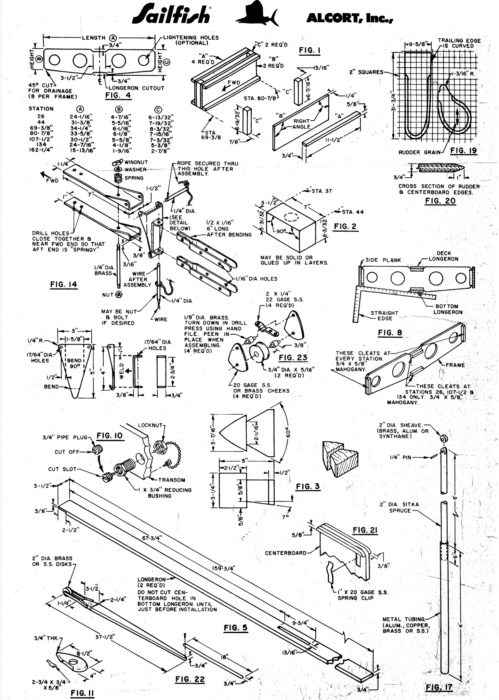 Laser Performance
Laser PerformanceSuper Sailfish parts
The kit assembly instructions can be found in the Files section of the Sunfish Sailor Yahoo group (after joining the group) and are very helpful when repairing wooden Sailfish, or for building a new Sailfish from the plans, found in the same Files. Sunfish sails and spars to fit the Super Sailfish can be ordered from Sunfish Direct. The Sunfish is manufactured in fiberglass by Laser Performance.
Is there a boat you’d like to know more about? Have you built one that you think other Small Boats Magazine readers would enjoy? Please email us!












Let’s build one FOUR times original size! What a hoot! May have to reduce sail area proportionally….just imagine the fun! Or take one to J boat size! Wow!
Great article. Love the video to see how it sailed. But most of all, really enjoyed reading the history behind the ubiquitous Sunfish, which I have sailed often over the years. The wooden Sailfish versions were before my time. Thank you.
We have a mini sunfish that we bought used in the 1980’s. It is a sturdy craft, and we have
sailed it a lot over the years down here in the Florida Panhandle. I repainted it with Interlux fifteen years ago, and it still looks good. It seems to be indestructible.
I am thinking of making a longer dagger board for her, after reading the excellent article in
Small Boats. Anybody know where I can get a new handle?
It’s interesting how things come around.
Al and Cort first built the Sailfish as a paddleboard to go after swimmers as they were trying for a Red Cross contract. An enlarged surfboard if you will. Too expensive for the Red Cross. So what to do with it. Besides iceboats, Al and Cort were open canoe sailors, and presumably had some kit kicking around. Doesn’t take much to put the two together. The LIFE article came about by some kind of friend-of-a-friend-girlfriend relationship. Don’t remember the details. In today’s saturated world it is difficult to think of a media splash that would have the same impact as a multiple page spread in LIFE. Not so incidentally Al and Cort created the first fully self-rescuable sailing craft.
The Sunfish apparently happened when either Al’s or Cort’s wife became pregnant and found the Sailfish hard to sail.
And it is interesting to see that the Sailfish does work pretty well as a paddleboard!
I got mine as a 13th-birthday present from my grandmother, back in 1967, and sailed her on Cranberry Lake in NW New Jersey. My evil trick was to grab a gust, haul in, then climb over the side to stand on the daggerboard, dumping my crew in the middle of the lake. I could right her and be off again before they knew what was happening.
Nice useful information here. I just purchased an early ’70s MK II. Ready to start cleaning it up. Question: there is a small (3/8″ – 1/2″) hole located next to the bow handle on the deck. Any idea what it’s for? A drain of some type maybe? Any help would be appreciated.
The Alcort Sailfish and Sunfish featured in your current issue are wonderful boats! The underlying philosophy of fun, simplicity and low cost, coupled with ease of transport and storage, would have given access to sailing to many, many people who otherwise would never have had an experience of the sport.
You might be interested to know that the influence of these boats spread far and wide. In 1956 in Melbourne, Australia, two friends, Bruce Scott and Jack Carroll, were both keen dinghy racers and came across some articles in North American yachting magazines that featured the Alcort Sailfish and Sunfish. The articles provoked their immediate interest – no crew worries, just rig ’em and race ’em. Those articles were the stimulus for their design of a sailboard that could be easily home-built and which was suitable for the notoriously challenging conditions of Port Phillip Bay. This became the Australian Sailfish.
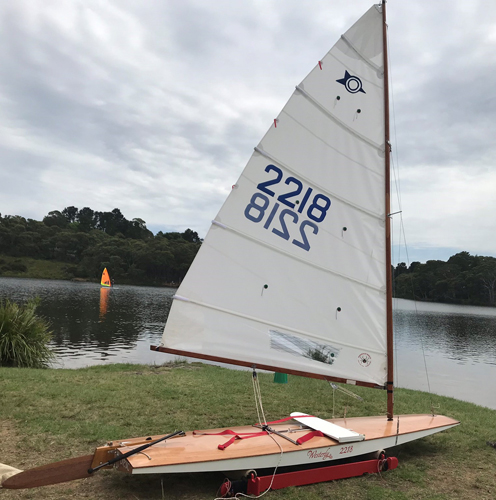

The Australian Sailfish very quickly became popular at clubs on Port Phillip, and then spread rapidly through the eastern states of Australia and onto Papua New Guinea. An Australian Sailfish Class Owners Association was formed in 1961. National championships commenced in 1968 and were held annually thereafter.
The Alcort Sailfish and Sunfish were undoubtedly the stimulus for this Australian boat. The Australian boat is of similar overall dimensions to the Alcort Sailfish, and has the same sail area. It is a distinctly different craft to the North American boat, however, in that it is considerably lighter (minimum hull weight 63 lbs), has a stayed, fully-battened Bermudan rig, and, importantly, is a scow. These features probably allow it to point higher and plane earlier and faster than the Alcort boat (but at the cost of some of the simplicity of the original design).
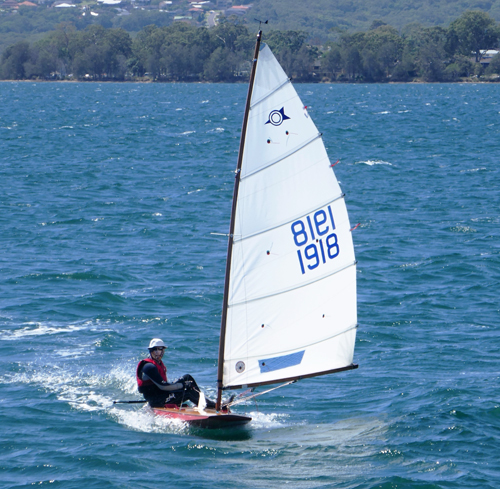


They certainly provide for exciting, close and high performance racing.
Sadly, like so many of the wooden racing dinghy classes in Australia, the number of Australian Sailfish competing at club level declined dramatically in the 1980s, and the class association folded in 1988.
Pleasingly however, there has been a wooden-boat renaissance in Australia over the past decade or so, and this has lead to a revival also of the Australian Sailfish. There have been fleets of ten to twenty Sailfish participating at wooden-boat regattas over the past few Australian summers. There have been new builds, plans have been distributed worldwide, and there have been three Australian Sailfish built in the past year in the USA in Florida, Wisconsin, and San Francisco. This revival has been promoted and reflected by an Australian Sailfish website, of which I am a co-administrator. Jack Carroll remains well and active at 90 years of age, and was in fact awarded with an Order of Australia in June this year for services to sailing.
In June this year, I was fortunate to attend the WoodenBoat Show at Mystic Seaport, something I’ve wanted to do for many years. While there, I visited the museum’s small-boat collection. I was on a mission. Just inside the entrance was the Alcort Sunfish, racked up with its stablemate, the Laser. I went exploring further, and, to my delight, I found the Alcort Sailfish tucked away in a back corner of the collection. It was a thrill.
Several days later, by chance, I was able to hire a Sunfish on the beach at Chatham on Cape Cod, and sail it on the waters of Nantucket Sound. That was a great thrill!
I hope that this information might be of some interest to you. Thank you for your wonderful magazine.
Would anyone like to buy an early model of the Super Sailfish that is in great shape?
Yes!
In the late ’50s and early ’60s we would sail with a neighbor on his Sunfish in Lake Michigan. Usually, sailing was a lot of fun, except for the day when small-craft warnings were posted, and we capsized, breaking the aluminum mast against the sand.
Great article.
I had a Sailfish and sailed Lake Ontario and some northern Ontario lakes with it from 1975 to 1991. It was faster and more athletic to sail than the Sunfish that we also had. I wish they were still available.
We rented a Sunfish 1966 and sailed it on Lake Simcoe near Big Bay Point. I convinced our family to buy one the next year. Sailed it at our rented cottage on Lake Simcoe and Lake Ontario from the Silver Birch Boathouse in east-end Toronto beaches for the next 9 years. Then was invited to race International 14 and Thunderbird yachts because of my Sunfish experience. Now I’m back in Sunfish racing in Canandaigua Lake and Rochester. Love going out in my Sunfish when the wind is too much for other boats.
A couple of answers.
1. For a replacement Minifish daggerboard I’d watch eBay for a “Barrington” board. If the desire is to make new handles, cut some 3/4″-square cleats and screw them to the top of the new, longer daggerboard.
2. The hole up by the bow handle was for a drain plug.
My first boat was a Masonite Sailfish (1974). The drain plug was in the transom, and it had wooden spars, grab rails, mast step, etc., and an old cotton sail. I varnished all the wood, and painted her international orange with a white cockpit – don’t laugh, it looked great with the varnished accents! The first time I capsized her, I was petrified, but then my feet hit the bottom! Shallow water! One time she just refused to tack, and when I got her home, found out that the stern drain plug had not been screwed in, and she weighed about 500 pounds. Many other newbie stories with that boat. Great fun always.
If you guys wanted to go back in time, my grandfather co-invented the Sunfish.
Here is a poem I wrote about it:
Sunfish
A Maple leaf floated on the lake
Momentum pushed it into a breeze
Cortlandt watched it slowly drift by, tacking south
The wheels in his head started turning
Shorter, he thought, if the boat is shorter, it will turn more sharply
It will be an easier boat for play
In time, it was, and they were sold worldwide
But for now, Bud tried to manipulate a sheet of paper into an airplane
He wanted to see if he could hit the leaf
Nailed it
Murray Dunlap
“Next to a brain injury, the devil is a clawless kitten.”