Never mind that until grounding on a mudflat less than 30 miles from the finish line, SCAMP #4 breezed through a difficult year in the 300-mile Everglades Challenge adventure race a few years ago, pressing on comfortably when many bigger boats had to quit. Never mind that during the inaugural Race to Alaska earlier this year, SCAMP #11 completed a very rough 40-mile open-water crossing of the Strait of Juan de Fuca, taking its solo skipper safely from Port Townsend, Washington, to Victoria, British Columbia. And never mind that yet another SCAMP (extensively modified for the venture by its builder) may attempt to round Cape Horn—yes, that Cape Horn—this year and, if successful, will be the smallest sailboat ever to do so. Despite all that, the overwhelming impression I get when Dave Ender drives up with his newly built SCAMP to take me sailing is: What a cute little boat.
 photographs and video by the author
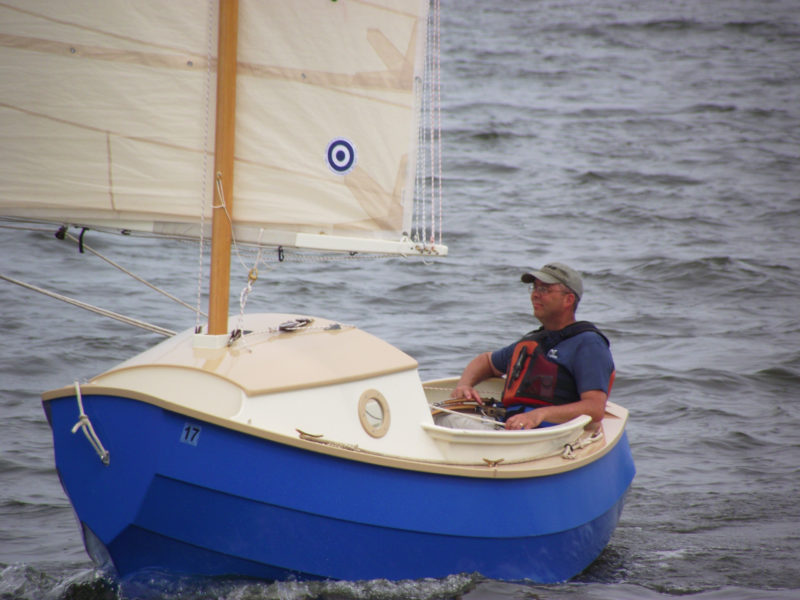
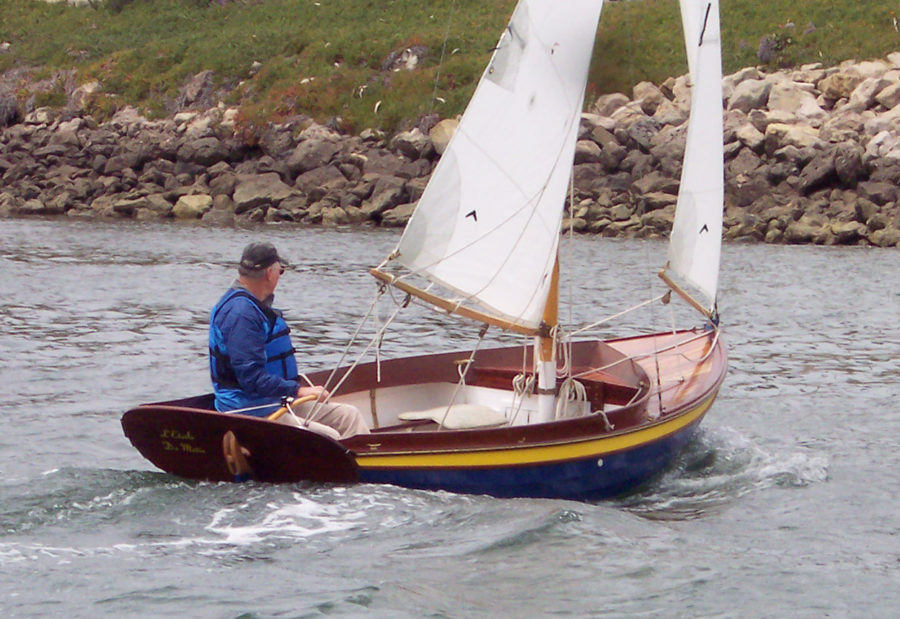
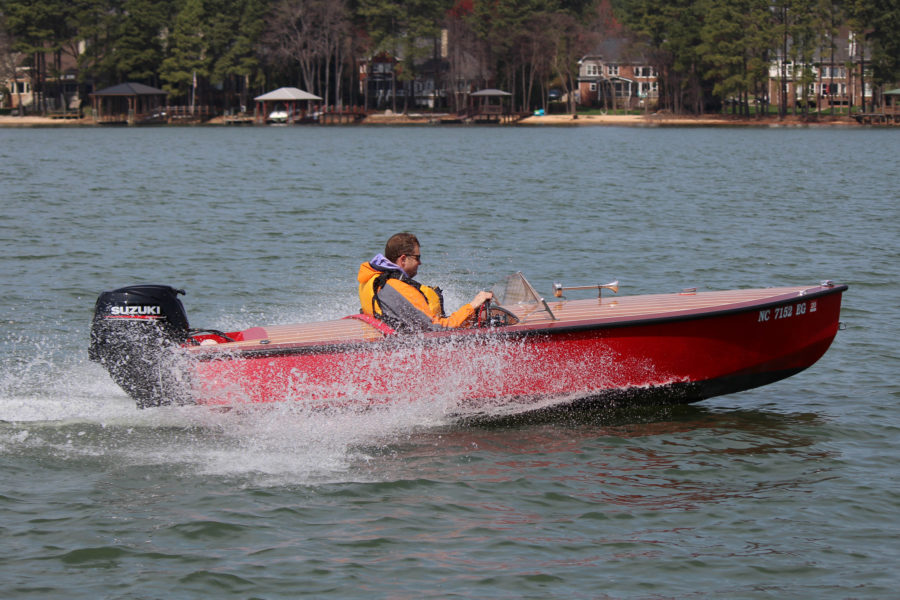
photographs and video by the authorThe buoyancy of the blunt pram bow resists digging in while running downwind and reduces the likelihood of broaching.
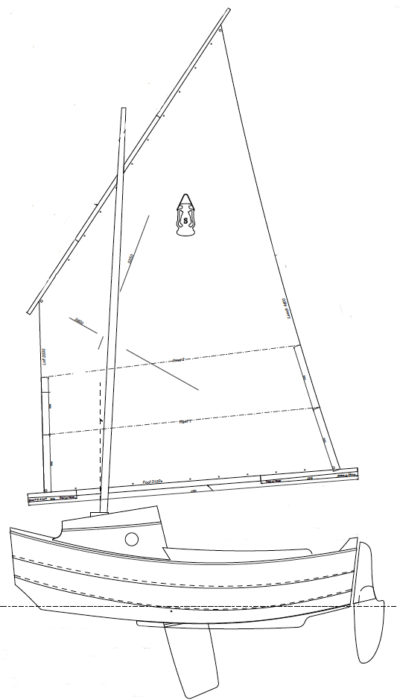
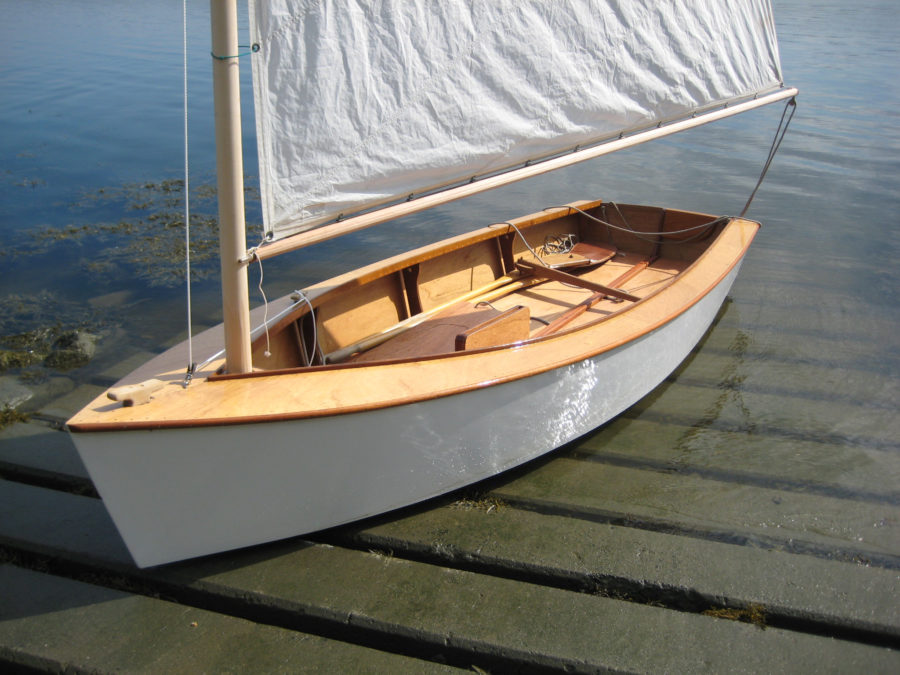
SCAMP is short, curvy, beamy, and high-sided, with a well-rockered flat bottom and a distinctive pram bow—a cross between a bulldog, a basketball, and an angry rubber duck. It’s also one of the easiest-launching boats I’ve ever encountered. I barely had time to grab my gear before Ender had the boat rigged and ready: mast stepped, sail hoisted, and rudder hung on the transom. He backed the trailer into the water and shoved SCAMP off. Less than 10 minutes from arrival and it was time to sail.
Josh Colvin, who commissioned SCAMP—an acronym for Small Craft Advisor Magazine Project—wasn’t looking for an ultimate adventure boat when he approached New Zealand designer John Welsford (see WB No. 225 for a profile on Welsford and his design work). “My initial goals for the boat were based largely on a 150-mile sail down the Columbia River, from Beacon Rock to Astoria,” Colvin says. “I kept coming across backwaters and shallow estuarine areas and thinking, That’s where I really want to go, but my 16-footer was too deep, wasn’t easy to row, and if I wanted to overnight up among the reeds, wouldn’t dry out level if the tide left. So the idea I eventually took to John Welsford was for the smallest possible boat that would be able to do all of these things, but still be seaworthy enough to cope with something like the middle of the Columbia River on a breezy afternoon.”
Judging by SCAMP’s popularity among amateur builders—roughly 340 kits or plan sets have been sold since 2011, with about 60 boats launched—plenty of other people are interested, too. Designer John Welsford sees SCAMP as a sort of 21st-century version of a much-loved classic, the Mirror dinghy. “While we don’t expect to do anywhere near as many boats,” Welsford says, “it’s hitting a similar, but older market.” Along the way, SCAMP has fostered an enthusiastic and supportive community of builders and owners, encouraging new builders to take the plunge.
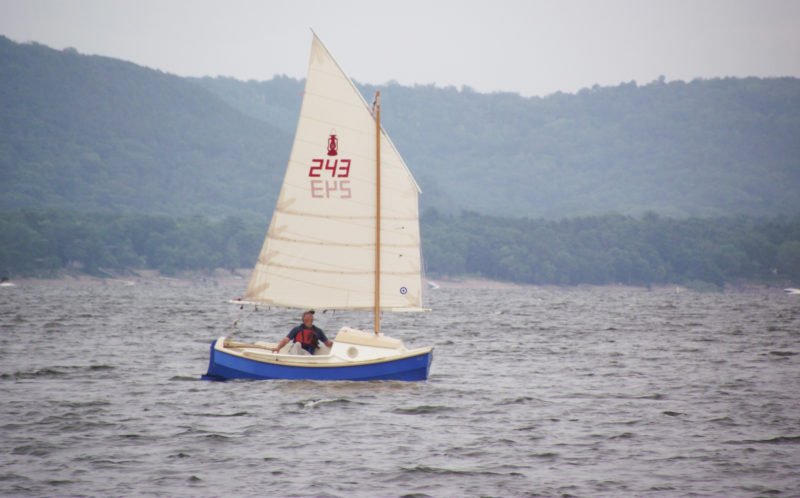

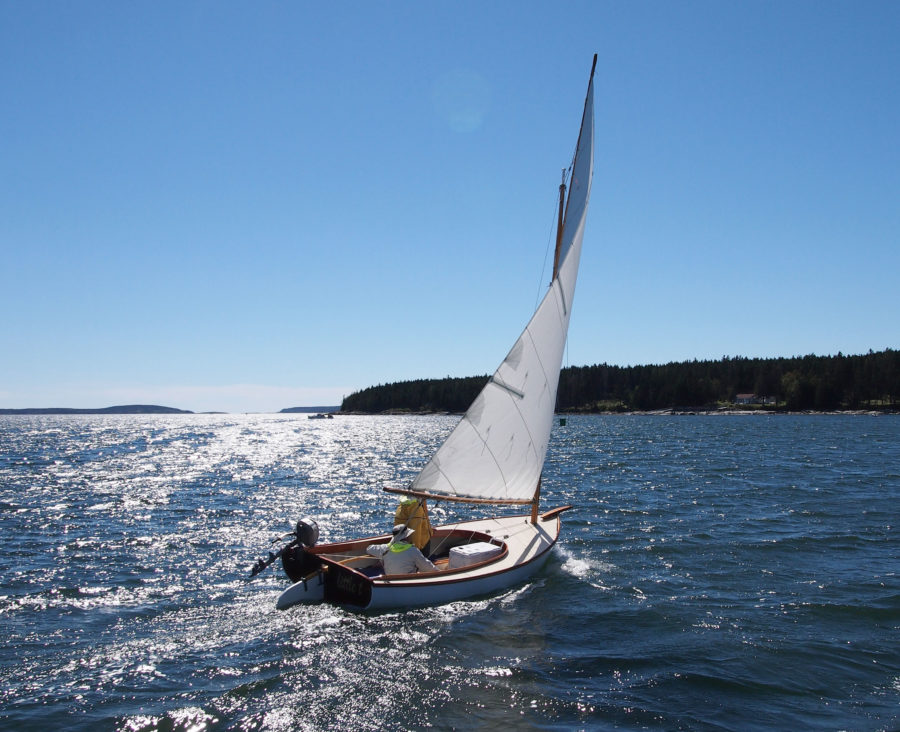
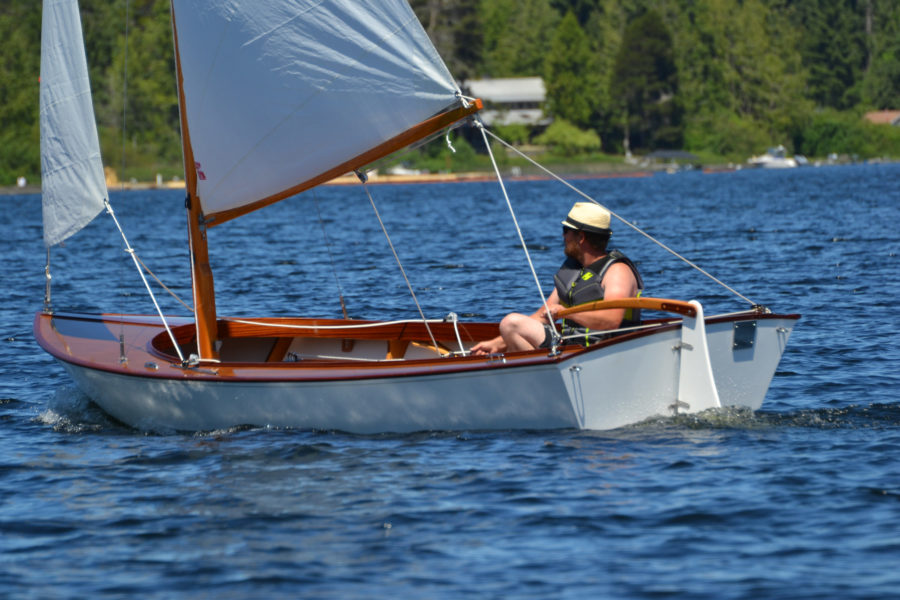
The SCAMPS’s 100-sq-ft sail is set high for good visibility under the boom and is easily reefed.
To bring the new design to life, Welsford was able to make good use of his previous experimentation with similar boats. “SCAMP is number six in a series of very beamy, shallow-bodied boats with that distinctive high-positioned pram bow,” Welsford says. “Tender Behind, Tread Lightly, and Sherpa are the other designs that made it to plans. All work really well, can carry huge loads for their size, sail well, and are well balanced. I learned something from each of them, and SCAMP is a result of that learning.” Besides Welsford, boatbuilder/designer Kees Prins of Port Townsend, Brandon Davis of Turnpoint Design, and adventurer/prototype tester Howard Rice all contributed to final design details and kit elements for SCAMP.
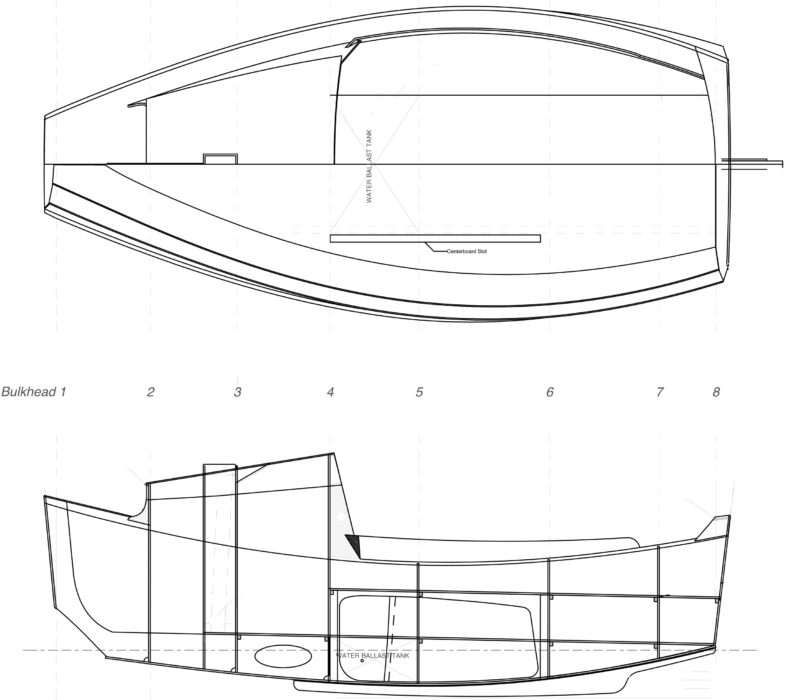
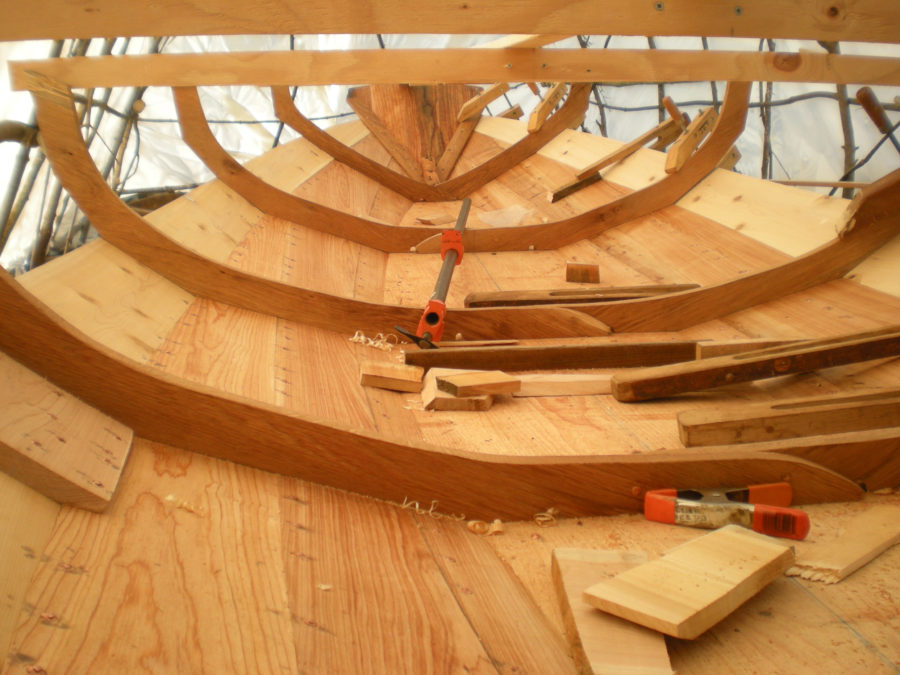
SCAMP is built upright on its flat bottom, which serves as the base for an egg-crate arrangement of plywood that forms the boat’s furniture and structural members. No temporary molds or frames are used. It’s a method that makes for an exceptionally stiff hull, and a safe one—the completed “boxes” create six entirely separate buoyancy chambers within the glued-plywood lapstrake hull. Welsford reports that one SCAMP was able to remain comfortably afloat despite suffering “a hole in the side that you could put your head through” after hitting a snag. And although there are plenty of parts to assemble when building a SCAMP, no single step requires more than moderate woodworking skills and a selection of basic tools.
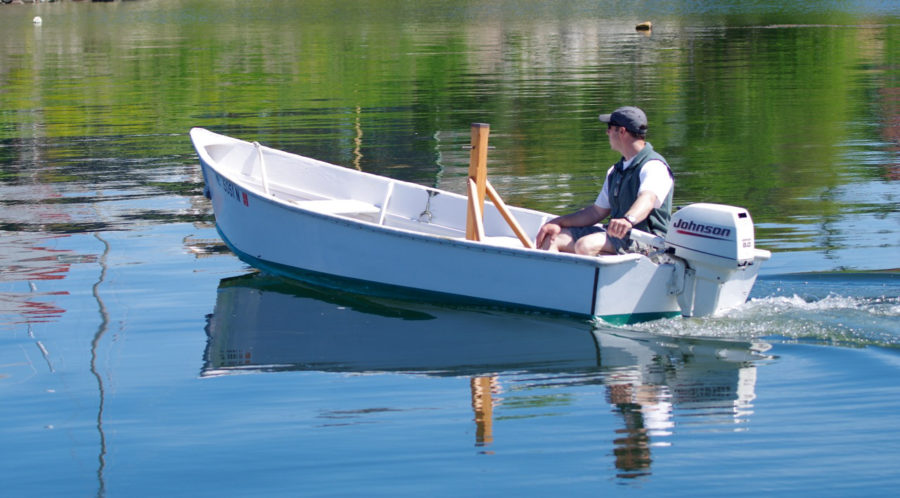
SCAMP is rigged with a single balanced lugsail, an excellent choice for a cruising rig that’s simple to handle and easy to reef. With 100 sq ft of sail and the stability to stand up to it, the boat also performs well. On my second sail in a SCAMP, working to windward on a gusty day, I was able to keep ahead of a 21′ Sea Pearl for several miles. SCAMP’s shallow draft and flat bottom make it a perfect gunkholer, and 173 lbs of water ballast (roughly 40 percent of the total hull weight) make it capable of much more. It’s no pulling boat, but SCAMP won’t be too difficult to move under oars when necessary. Some builders have considered experimenting with a single sculling oar at the transom; Dave Ender plans to try a yuloh. There’s room to mount a small outboard on the transom for backup propulsion.
Builders have the choice of building from plans or from a kit, with custom sails and hardware available for purchase. Another popular option for builders is the SCAMP Camp, a two-week intensive class in which participants come together to assemble their own SCAMP kits under the direction of designer John Welsford and prototype tester Howard Rice.
One unintended feature of the design deserves mention: several SCAMP builders I have met describe the boat as “a chick magnet,” and from my own observations at various messabouts and festivals, I’d say that such a claim is closer to reality than to hype. For potential builders with wives or girlfriends reluctant to take up sailing, this might be the single biggest advantage SCAMP has to offer.
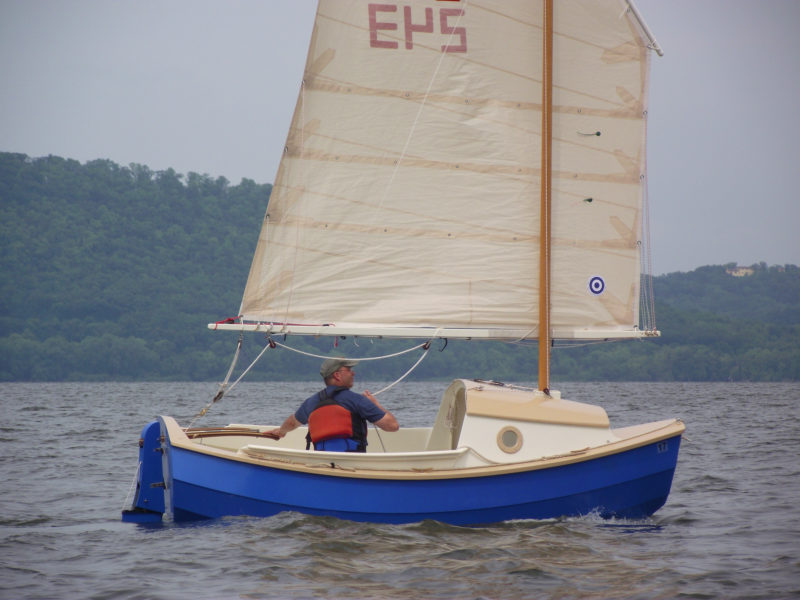

A kick-up rudder allows sailing in shallow water and twin skegs help the SCAMP sit solidly upright when grounded.
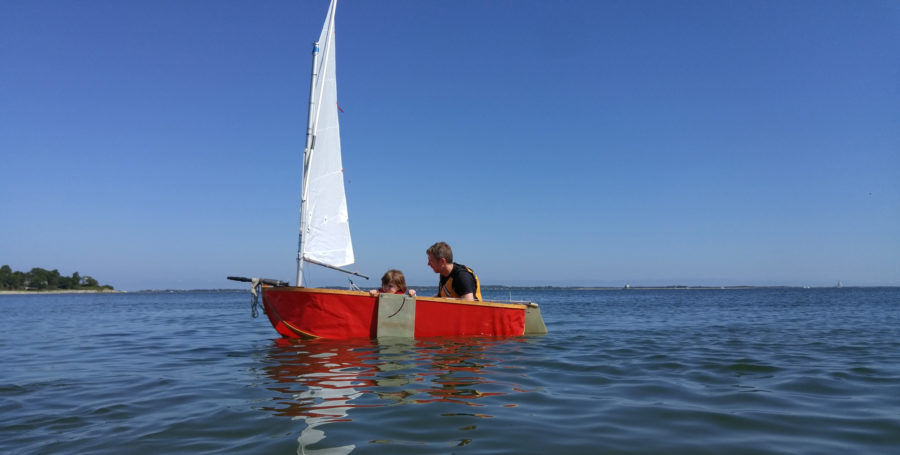
Back aboard Dave Ender’s Scamp, we were away from the dock with an easy shove, heading across Lake Pepin, a wide stretch of the Mississippi that’s often subject to strong winds sweeping down between tall bluffs. Dave filled the ballast tank under the cockpit sole. With the drain holes open, the tank floods itself almost completely; the top of the tank is a few inches above the waterline, so must be topped off by replacing the plugs and pouring water in with a bucket from the cockpit before sealing. He could pour water in quickly without worrying about spilling or overflowing: The excess water drains out of the cockpit’s scuppers. With the water ballast in, we soon shook out the reef we started with, and Dave put me at the tiller. It was a windy day, but even under full sail we continued on in perfect comfort. SCAMP may be a small boat, but it’s the biggest small boat I’ve ever sailed. In fact, it’s almost impossible to categorize SCAMP by size. It weighs just over 400 lbs empty, but has the cockpit and freeboard of a 20′ keelboat (in fact, the freeboard is so high that reboarding the boat without a pre-rigged foot stirrup or rudder step would be problematic). It’s easy to drag up a SCAMP onto a beach for a quick stop ashore, yet filling the ballast tank adds stability well beyond the reach of a typical small boat. The self-draining cockpit sits high enough above the water that you feel like you’re aboard a much bigger boat—yet SCAMP is extremely maneuverable, tacking easily and spinning around within its own length like the smallest dinghy.
While it performs well enough to keep experienced sailors interested—Dave and I kept pace with several much bigger keelboats without much trouble—SCAMP would also be a great boat for beginners to learn on. The balanced lug makes tacking or jibing very simple and stress-free; lazyjacks hold the sail and boom securely in place, making reefing easy once the lines and cleats are set up; the boat is stable and comfortable. And it’s pure fun to sail. The only thing that I needed some time to get used to was being so far from the water compared to the sail-and-oar boats I usually sail. Of course, that higher freeboard and greater volume help make it easy to recover from a capsize (see the video below). By the time Dave and I returned to the dock, I was reminded again of just how much I like this design, and how much it can do.

The diminutive SCAMP is easily trailered, rigged, and launched.
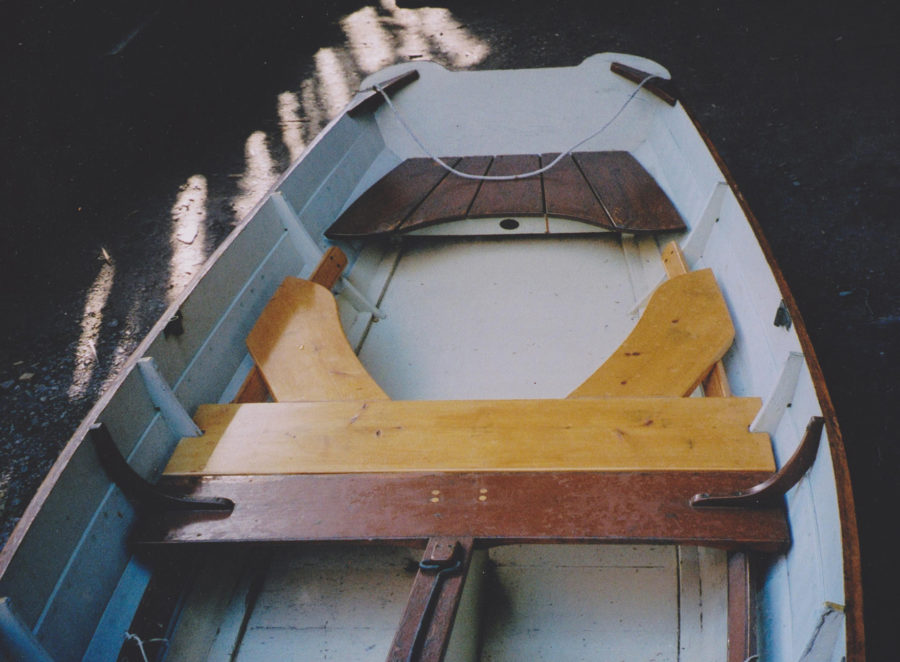
With its quick launching capabilities, SCAMP would work well as a family-friendly daysailer. There is space enough for four adults in relative comfort (three is better; two is luxurious), and the boat’s stability makes it a comfortable ride even for the elderly and infirm, young children, or passengers who might simply be a bit nervous around boats. The boom is high overhead, minimizing the risk of hitting an inexperienced passenger, and the seats are wide and comfortable.
Cruising solo or two-up is where SCAMP really shines. The 8′3″ x 29″ cockpit sole provides ample space for one person to sleep aboard very comfortably (the offset centerboard is hidden in the starboard seat face), and filler planks between seats can be used to create a double bunk. The benches themselves (6′8″ by 17.5″) offer a place to stretch out but aren’t quite wide enough for sleeping. There is plenty of stowage space under the seats and cockpit. The “veranda” (a small cuddy/locker at the forward end of the cockpit) provides additional stowage, sitting headroom, and shelter from the wind, as well as a convenient place to anchor the forward edge of a cockpit tent. Forward of the veranda’s bulkhead there are 8.5 cubic feet of sealed stowage that provide extra buoyancy well above the waterline, just where it would be most useful in a knockdown. And of course, like all small boats, a SCAMP can easily travel to windward at 60 mph, pulled on a small lightweight trailer by a small four-cylinder car.
All in all, SCAMP is an unusual boat—an odd duck, both in appearance, and in its strange synthesis of big and small. It’s part keelboat, part dinghy, and part semi-eccentric fashion statement. Make no mistake, though; SCAMP is plenty of boat, wherever your interests lie. Anyone who builds one will definitely find plenty of ways to use it, and plenty of people to use it with. And that, after all, is the point of having a boat in the first place.![]()
Tom Pamperin (www.tompamperin.com) is a frequent contributor to Small Boats Monthly and WoodenBoat.
SCAMP Particulars
[table]
LOA/11′11″
Beam/5′4″
Draft (board up)/7″
Weight (including rig)/420 lbs
Water ballast/173 lbs
[/table]
Plans and information are available from Small Craft Advisor. Their YouTube channel has several videos featuring the SCAMP, including a capsize trial with Howard Rice, below.
Is there a boat you’d like to know more about? Have you built one that you think other Small Boats Monthly readers would enjoy? Please email us!


























Great article! Thanks. I especially enjoyed the fact that during the capsize test, Howard did not lose his hat! Now that’s a sailor. I’ve always been off put by the punt bow, but seeing the boat in action, I can now appreciate it.
That boat did not want to capsize…
Thanks for the kind words about the article; I enjoyed yet another excuse to go sailing aboard a Scamp. It’s a fun and very very capable little boat, that’s for sure.
Tom
These are great wee boats, totally sold on the concept especially the seaworthiness. The only thing I would do differently is wear a safety harness in winds like that in the video! I could quite easily see the boat sailing off while you flounder around in the briny!